Did you know nuts are tiny powerhouses bursting with health benefits? From supporting heart health to keeping you full between meals, nuts are a versatile addition to any diet. They’re easy to snack on, sprinkle in recipes, or grab on the go. If you’ve been hesitant to add nuts to your routine, consider this a friendly nudge in the right direction. Here’s why nuts deserve a spot on your plate, the unique benefits of various types of nuts, and a few easy ways to incorporate them into your meals.
The Health Benefits of Nuts
Nuts aren’t just delicious—they pack a serious nutritional punch. Full of healthy fats, protein, vitamins, and minerals, they’re one of nature’s most nutrient-dense foods. Here are some of the standout benefits you’ll gain from making nuts part of your daily diet.
1. Support Heart Health
Many nuts are rich in unsaturated fats, which are crucial for heart health. Unlike saturated fats, which can raise cholesterol levels, unsaturated fats work to lower LDL cholesterol (the “bad” kind) while increasing HDL cholesterol (the “good” kind).
Some nuts, like walnuts, are even high in Omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation and may lower your risk of cardiovascular disease. It’s no wonder studies consistently show that people who eat nuts regularly have a reduced risk of heart attack and stroke.
2. Aid in Weight Management
Contrary to popular belief, eating nuts won’t sabotage your weight-loss efforts. Their healthy fat and protein content helps keep you fuller for longer, which may reduce overall calorie intake. Plus, their crunchy texture and rich flavor make them a satisfying snack without the need for chips or cookies.
3. Provide Essential Nutrients
Nuts are brimming with vital nutrients like magnesium, vitamin E, selenium, and B vitamins. They also offer antioxidants that help fight free radicals, reducing oxidative stress in your body. Other micronutrients, like zinc and calcium, strengthen your bones and immune system.
4. Stabilize Blood Sugar Levels
For anyone monitoring their blood sugar or managing diabetes, nuts can be a helpful addition. The combination of protein, healthy fats, and fiber slows down digestion and prevents sudden spikes in blood sugar levels.
5. Promote Brain Health
Think of nuts as fuel for your brain. Thanks to their high content of Omega-3s and antioxidants, nuts like walnuts can help improve memory, cognitive function, and even reduce your risk of age-related conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Clearly, nuts are more than a tasty treat—they’re a wholesome way to invest in your health.
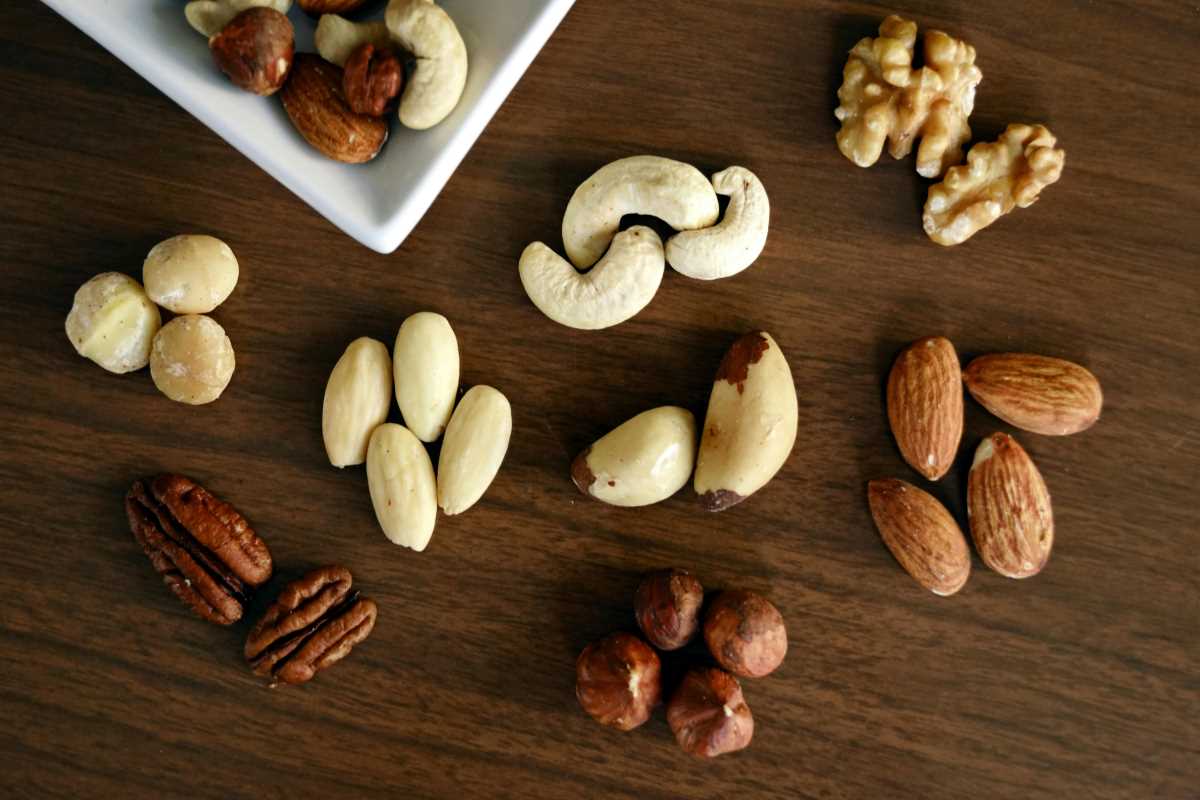
A Nut-by-Nut Breakdown
Not all nuts are created equal. Each type offers a unique set of benefits, so mixing things up will give you the broadest range of nutrients.
Almonds
- Benefits: High in vitamin E, magnesium, and calcium, almonds are a great choice for supporting bone health and skin health.
- Uses: Sprinkle slivered almonds over yogurt or oatmeal, or snack on a handful with a piece of fruit.
Walnuts
- Benefits: Packed with Omega-3 fatty acids, walnuts are brain food that also promotes heart health.
- Uses: Add walnuts to salads, baked goods, or a homemade trail mix.
Pistachios
- Benefits: Pistachios are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that support eye health. They’re also one of the lowest-calorie nuts, great for snacking.
- Uses: Enjoy them roasted and salted, or toss them into a grain salad like quinoa.
Cashews
- Benefits: Creamy and slightly sweet, cashews are high in copper, which is essential for energy production and collagen formation.
- Uses: Use cashew butter as a spread, or blend cashews into a dairy-free cream sauce.
Brazil Nuts
- Benefits: Just one or two Brazil nuts a day can provide all the selenium your body needs for proper thyroid function.
- Uses: Snack on them raw or chop them up as a topping for desserts.
Peanuts
- Benefits: Technically a legume, peanuts are rich in protein and biotin, which supports hair and skin health.
- Uses: Spread natural peanut butter on whole-grain toast for a quick and satisfying breakfast.
Including a variety of nuts in your diet ensures you get the best of what each has to offer.
How to Incorporate Nuts Into Your Daily Diet
Adding more nuts to your meals is easier than you might think. Whether you’re a culinary wizard or a fan of simple snacks, here are some practical ideas to get you started.
1. Snack Simply
There’s nothing wrong with enjoying nuts straight out of the bag. A small handful of almonds, cashews, or pistachios is a quick and portable snack that satisfies cravings while keeping hunger at bay.
2. Boost Your Breakfast
- Add crushed walnuts or sliced almonds to your oatmeal.
- Top your smoothie bowl with a sprinkle of chia seeds, flaxseeds, and your favorite nuts.
- Spread almond or peanut butter onto whole-grain toast with a drizzle of honey.
3. Get Creative at Lunch
- Toss a few pecans or pistachios into your salads for added crunch.
- Use cashews as the base for a creamy vegan sauce or curry.
- Blend roasted peanuts into a dressing for noodles or stir-fry.
4. Update Your Dinners
- Coat chicken or fish in a crushed-nut crust for extra flavor and texture.
- Top casseroles or roasted vegetables with chopped nuts for a finishing touch.
5. Sweeten Up Dessert
- Use crushed walnuts or pecans in baking for cookies, muffins, or brownies.
- Blend nuts into energy bites or granola bars for a healthy treat.
- Sprinkle roasted nuts over fruit parfaits or frozen yogurt.
By keeping a stash of nuts in your pantry, you’ll always have a way to elevate your meals and snacks.
The Importance of Portion Control
While nuts are incredibly nutritious, they’re also calorie-dense, thanks to their high fat content. Overindulging can lead to unintended weight gain, so it’s important to enjoy them in moderation.
Recommended Serving Sizes:
- Whole Nuts: About a small handful, or 1 ounce (roughly 23 almonds or 14 walnut halves).
- Nut Butter: 2 tablespoons are typically recommended as a serving.
To avoid overeating, portion out your nuts ahead of time instead of eating directly from the package.
Disclaimer: The content provided on SuperHealthyTips is for informational and educational purposes only. This information is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
 (Image via
(Image via


.jpeg)