Staying active is one of the best things you can do for your health at any age, but when you hit your mid-life years, your health goals might look a little different. It’s less about training for the Olympics and more about finding balance, staying strong, and supporting long-term well-being. One tool that middle-aged adults can use to stay on top of their fitness and heart health is heart rate zones. These zones give you insight into how hard your heart is working during exercise and help you make the most of your workouts without overdoing it.
Not sure where to start? Don’t worry; heart rate zones aren’t just for elite athletes. They’re for anyone who wants to work smarter, not harder, to protect their health. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
What Are Heart Rate Zones?
Heart rate zones are different ranges of beats per minute (bpm) that indicate how hard your heart is working during physical activity. These zones are divided into percentages of your maximum heart rate (MHR), which is simply the fastest your heart can safely beat.
Think of it as a personalized fitness guide. Each zone corresponds to different benefits, from fat-burning and endurance-building to heart health and peak performance. Knowing your heart rate zones can help you optimize your workouts for specific goals, like maintaining a healthy weight or improving cardiovascular health. Even better, they help ensure you’re exercising safely at a level that’s right for your body.
Why Do Heart Rate Zones Matter?
- Track Fitness Progress
Monitoring your heart rate during exercise helps gauge your cardiovascular health and fitness improvements over time.
- Avoid Overtraining
Staying within the right zone prevents you from pushing too hard, which could lead to injury or burnout.
- Maximize Efficiency
Whether you want to lose weight, improve stamina, or strengthen your heart, heart rate zones help you focus your efforts.
For middle-aged adults, paying attention to heart rate zones isn’t just smart—it’s essential. Your heart is a muscle, and like any muscle, it benefits from controlled, purposeful engagement.
How to Calculate Your Maximum Heart Rate
Before jumping into heart rate zones, you need to know your maximum heart rate (MHR). While there are advanced tests for pinpoint accuracy, there’s also an easy formula you can use:
Simple Formula:
220 – your age = MHR
For example, if you’re 50 years old:
220 – 50 = 170 bpm (your maximum heart rate).
Keep in mind, this is a general guideline. Factors like fitness level, medication, and overall health can affect your MHR, so it’s important to listen to your body as you work within these ranges.
Once you know your MHR, you can calculate your heart rate zones as percentages of that number.
Heart Rate Zone Breakdown:
- Zone 1 – Resting/Easy (50–60% of MHR): Light activity like walking or stretching falls in this zone. It’s great for recovery and overall health.
- Zone 2 – Fat-Burning (60–70% of MHR): Perfect for steady-state cardio; this zone targets fat as a primary energy source.
- Zone 3 – Cardio (70–80% of MHR): This zone improves stamina and cardiovascular strength. Think brisk walking, jogging, or cycling.
- Zone 4 – Peak Performance (80–90% of MHR): High-intensity interval training (HIIT) or vigorous exercise. Great for building speed and endurance but shouldn’t be sustained for long periods.
- Zone 5 – Max Effort (90–100% of MHR): All-out effort. Typically reserved for short bursts during advanced training. If you’re new to exercise, it’s best to avoid going this high.
Make sure you spend most of your workouts in Zone 2 or Zone 3 for long-term health benefits without overstraining your heart.
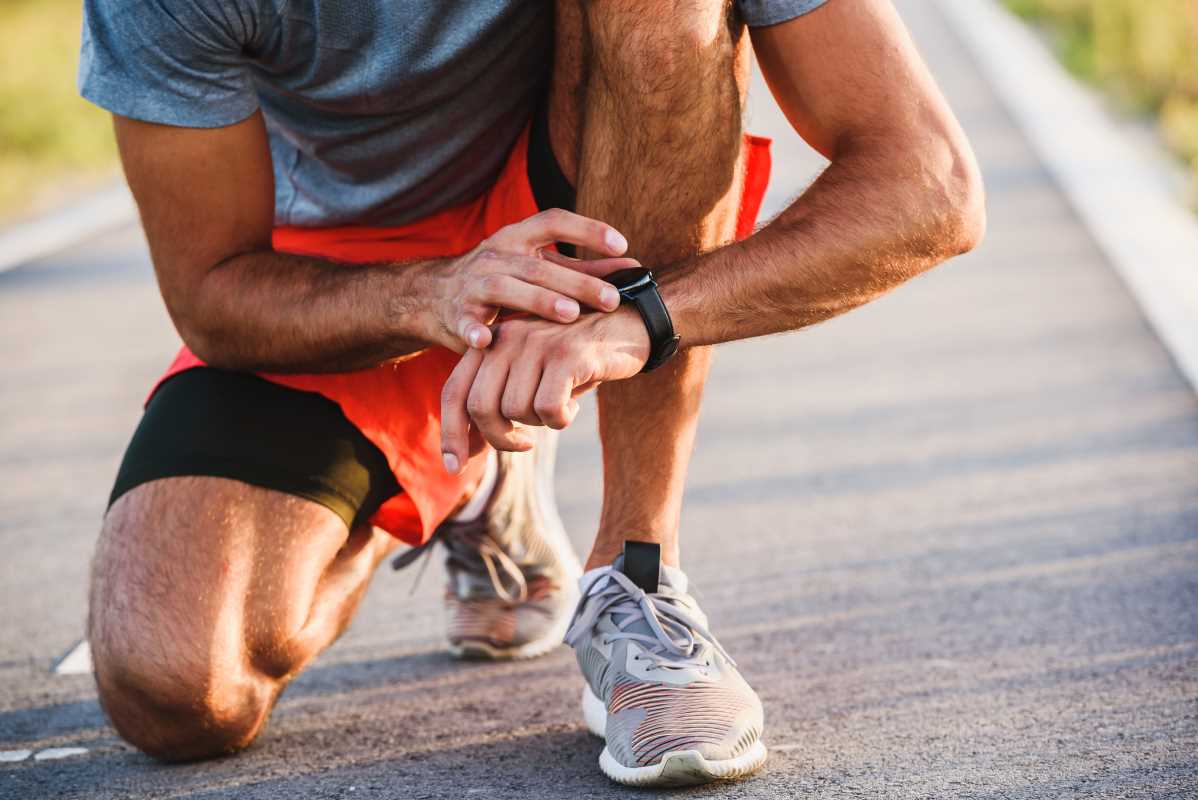
Tools to Help You Track Your Zones
Gone are the days of manually checking your pulse mid-workout. Several tools make tracking your heart rate zones easy and accurate.
1. Fitness Trackers and Smartwatches
Devices like Fitbit, Garmin, and Apple Watch come with built-in heart rate monitors and can even display which zone you’re in during activity. Some also provide insights into your fitness trends over time.
2. Chest Straps
For those who want more precise measurements, chest straps like the Polar H10 are considered the gold standard for heart rate tracking.
3. Apps
Pairing your fitness tracker or smartwatch with apps like MyZone or Strava can give you more detailed data and help you monitor progress toward fitness goals.
Pro tip? Look for devices or apps that allow you to customize your heart rate zones based on your MHR. This ensures you’re working in the ranges that are most beneficial for your health.
Tips for Using Heart Rate Zones in Your Workouts
Tracking your heart rate isn’t about staring at numbers the whole time you’re exercising. It’s about using that information to work smarter and more efficiently. Here are some practical tips to get started:
1. Start Slow
If you’re new to exercise or getting back into it after some time off, ease into Zone 2 activities like brisk walking or gentle cycling. These are low-impact but still offer great benefits for your heart and overall health.
2. Incorporate Variety
Alternate between zones to keep things interesting and challenge your body in different ways. For example:
- 20 minutes in Zone 2 (steady-state cardio)
- Intervals in Zone 3 and Zone 4 (1–2 minutes of high intensity, followed by recovery in a lower zone).
3. Listen to Your Body
Heart rate zones are guidelines, but they’re not the only indicator of how you’re doing. If you’re struggling to breathe, feeling faint, or experiencing pain, it’s time to dial back—even if you’re technically in the “right” zone.
4. Use It for Recovery
Heart rate zones aren’t just for workouts—they can also help you recover. After exercising, monitor how quickly your heart rate returns to normal. Faster recovery rates indicate improved fitness levels.
5. Pair with Lifestyle Changes
Combine heart rate zone training with good nutrition, adequate hydration, and quality sleep for the best results. Remember, your heart health depends on more than just exercise.
Benefits of Heart Rate Zone Training in Midlife
Why should middle-aged adults pay special attention to heart rate zones? Here are just a few of the many benefits tailored to your stage of life:
- Protects Against Overtraining
Your body’s recovery time changes with age. Staying within safe zones helps prevent injuries or exhaustion.
- Promotes Healthy Aging
Cardiovascular exercise in Zones 2 and 3 helps improve circulation, boost energy, and enhance overall quality of life.
- Supports Weight Management
Training in the fat-burning zone can help you maintain a healthy weight without feeling like you’re “maxing out.”
By making heart rate zones part of your fitness routine, you’re giving your body what it needs to stay strong and resilient for years to come.
Disclaimer: The content provided on SuperHealthyTips is for informational and educational purposes only. This information is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.




.jpeg)